Yes the data is unique to every device. There is no standard format, speed, or serial port data format. All devices pick and choose so you cannot assume code from device A would have any hope of working with device B from a different manufacturer. As was mentioned RS-485 defines the electrical communication. EIA-485, also known as TIA/EIA-485 or RS-485, is a standard defining the electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers for use in balanced digital multipoint systems. This standard is widely used for communications in industrial automation because it can be used effectively over long distances and in electrically noisy environments.
Shows how to use the synchronous API of QSerialPort in a worker thread.
Blocking Master shows how to create an application for a serial interface using the synchronous API of QSerialPort in a worker thread.
QSerialPort supports two programming alternatives:
- The asynchronous (non-blocking) alternative. Operations are scheduled and performed when the control returns to the Qt event loop. The QSerialPort class emits a signal when the operation is finished. For example, the write() method returns immediately. When the data is sent to the serial port, the QSerialPort class emits the bytesWritten() signal.
- The synchronous (blocking) alternative. In headless and multithreaded applications, the wait method can be called (in this case, waitForReadyRead()) to suspend the calling thread until the operation has completed.
In this example, the synchronous alternative is demonstrated. The Terminal example illustrates the asynchronous alternative.
The purpose of this example is to demonstrate how to simplify your serial programming code without losing the responsiveness of the user interface. The blocking serial programming API often leads to simpler code, but it should only be used in non-GUI threads to keep the user interface responsive.
This application is the master which demonstrates the work paired with the slave application Blocking Slave Example.
The master application initiates the transfer request via the serial port to the slave application and waits for response.
MasterThread is a QThread subclass that provides API for scheduling requests to the slave. This class provides signals for responding and reporting errors. The transaction() method can be called to start up the new master transaction with the desired request. The result is provided by the response() signal. In case of any issues, the error() or timeout() signal is emitted.
Note, the transaction() method is called in the main thread, but the request is provided in the MasterThread thread. The MasterThread data members are read and written concurrently in different threads, thus the QMutex class is used to synchronize the access.
The transaction() method stores the serial port name, timeout and request data. The mutex can be locked with QMutexLocker to protect this data. The thread can be started then, unless it is already running. The wakeOne() method is discussed later.
In the run() function, the first is to lock the QMutex object, then fetch the serial port name, timeout and request data by using the member data. Having that done, the QMutex lock is released.
Under no circumstance should the transaction() method be called simultaneously with a process fetching the data. Note, while the QString class is reentrant, it is not thread-safe. Thereby, it is not recommended to read the serial port name in a request thread, and timeout or request data in another thread. The MasterThread class can only handle one request at a time.
The QSerialPort object is constructed on stack in the run() method before entering the loop:
This makes it possible to create an object while running the loop. It also means that all the object methods are executed in the scope of the run() method.
It is checked inside the loop whether or not the serial port name of the current transaction has changed. If this has changed, the serial port is reopened and then reconfigured.
The loop will continue to request data, write to the serial port and wait until all data is transferred.
Warning: As for the blocking transfer, the waitForBytesWritten() method should be used after each write method call. This will process all the I/O routines instead of the Qt event loop.
The timeout() signal is emitted if a timeout error occurs when transferring data.
There is a waiting period for response after a successful request, and then it is read again.
Warning: As for the blocking alternative, the waitForReadyRead() method should be used before each read() call. This will processes all the I/O routines instead of the Qt event loop.
Rs232 Vs Rs485
The timeout() signal is emitted if a timeout error occurs when receiving data.
When a transaction has been completed successfully, the response() signal contains the data received from the slave application:
Afterwards, the thread goes to sleep until the next transaction appears. The thread reads the new data after waking up by using the members and runs the loop from the beginning.
Running the Example
To run the example from Qt Creator, open the Welcome mode and select the example from Examples. For more information, visit Building and Running an Example.

See also Terminal Example and Blocking Slave Example.
© 2020 The Qt Company Ltd. Documentation contributions included herein are the copyrights of their respective owners. The documentation provided herein is licensed under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License version 1.3 as published by the Free Software Foundation. Qt and respective logos are trademarks of The Qt Company Ltd. in Finland and/or other countries worldwide. All other trademarks are property of their respective owners.
1. Introduction¶

2. Hardware-related Considerations¶
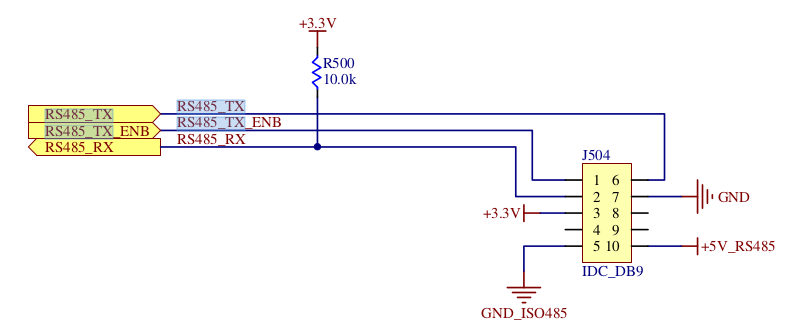
Some CPUs/UARTs (e.g., Atmel AT91 or 16C950 UART) contain a built-inhalf-duplex mode capable of automatically controlling line direction bytoggling RTS or DTR signals. That can be used to control externalhalf-duplex hardware like an RS485 transceiver or any RS232-connectedhalf-duplex devices like some modems.
For these microcontrollers, the Linux driver should be made capable ofworking in both modes, and proper ioctls (see later) should be madeavailable at user-level to allow switching from one mode to the other, andvice versa.
3. Data Structures Already Available in the Kernel¶
Rs485 Pinout
The Linux kernel provides the serial_rs485 structure (see [1]) to handleRS485 communications. This data structure is used to set and configure RS485parameters in the platform data and in ioctls.
The device tree can also provide RS485 boot time parameters (see [2]for bindings). The driver is in charge of filling this data structure fromthe values given by the device tree.
Any driver for devices capable of working both as RS232 and RS485 shouldimplement the rs485_config callback in the uart_port structure. Theserial_core calls rs485_config to do the device specific part in responseto TIOCSRS485 and TIOCGRS485 ioctls (see below). The rs485_config callbackreceives a pointer to struct serial_rs485.
4. Usage from user-level¶
From user-level, RS485 configuration can be get/set using the previousioctls. For instance, to set RS485 you can use the following code:
5. References¶
Rs485 Serial Cable
[1] include/uapi/linux/serial.h
[2] Documentation/devicetree/bindings/serial/rs485.txt
